Our Blog
The A-Z of Photography: Capturing Life Through the Lens
- July 24, 2023
- Posted by: Semilore Adelola
- Category: Photography Tips
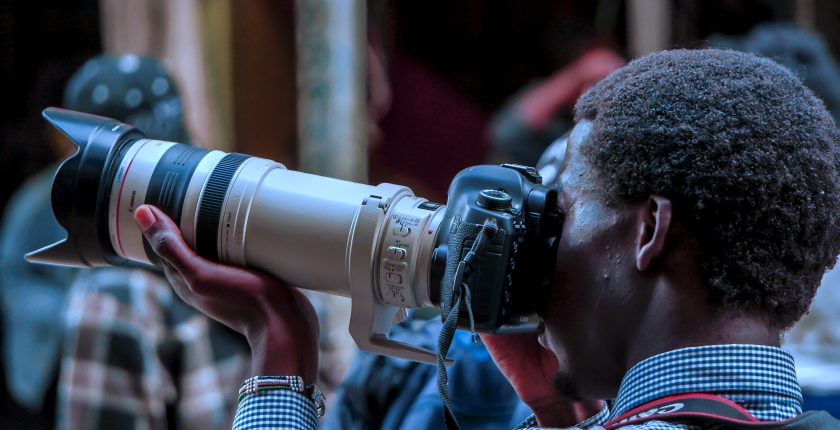

Welcome to the fascinating world of photography! As you embark on your photographic journey, you will discover the A-Z of photography – from the basic concepts to advanced techniques, from the history of photography to the latest trends and innovations. Whether you’re a beginner looking to understand the fundamentals or a seasoned pro seeking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with valuable insights and knowledge to excel in this art form.
A – Aperture:
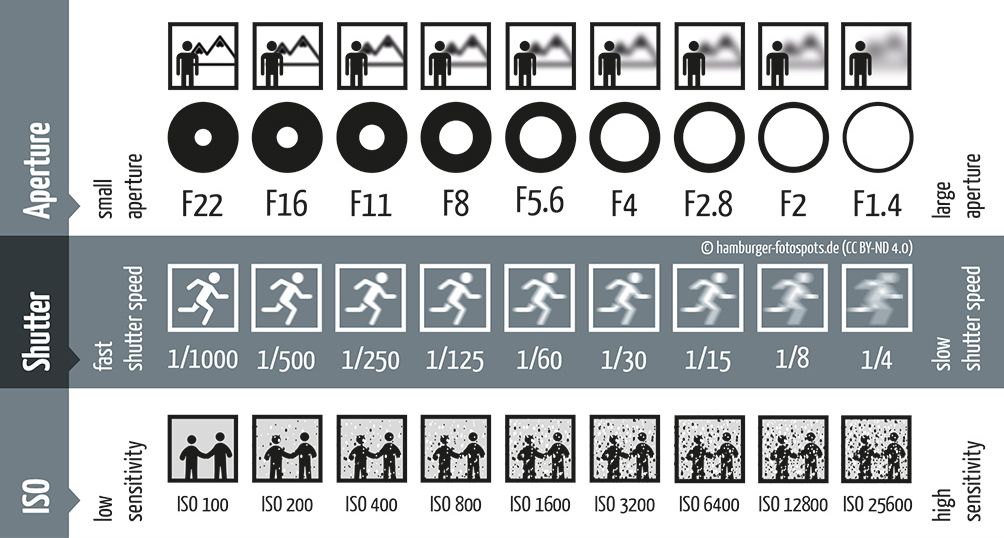
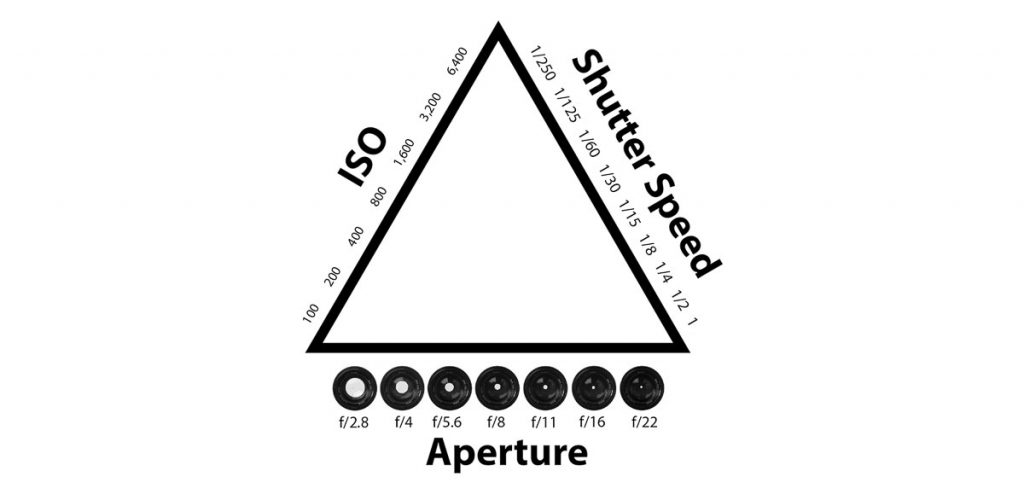
Let’s start with the basics. Aperture refers to the opening in the lens through which light enters the camera. It is denoted by f-numbers (e.g., f/2.8, f/8). A smaller f-number indicates a larger aperture, allowing more light to enter, resulting in a shallow depth of field. Conversely, a higher f-number means a smaller aperture, leading to a larger depth of field.
B – Bokeh:
Bokeh is the pleasing out-of-focus background achieved by using a shallow depth of field. This effect is highly sought after in portrait and nature photography, creating a dreamy and artistic feel to the images.
C – Composition:
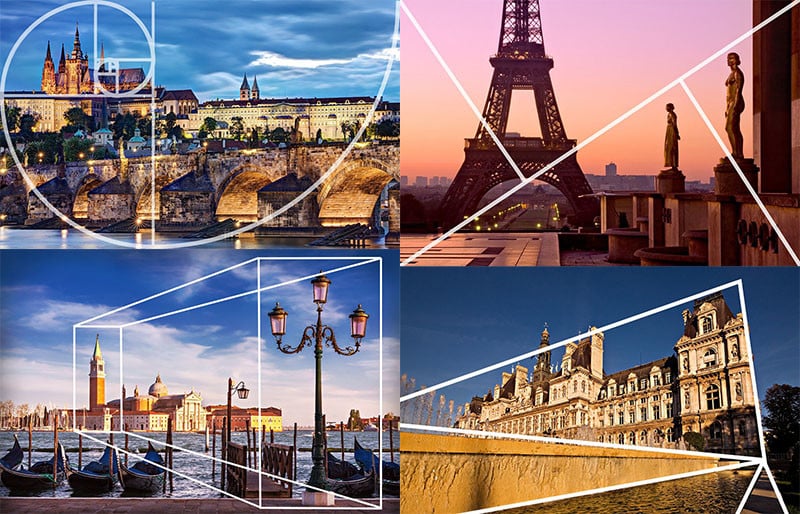
Composition is the arrangement of elements within a photograph. Learning how to position subjects, use leading lines, and balance visual weight is crucial in creating captivating and well-balanced images.
D – DSLR:

Digital Single-Lens Reflex cameras are popular among photographers due to their versatility, image quality, and interchangeable lenses.
E – Exposure:
Exposure refers to the amount of light that reaches the camera sensor. Achieving the correct exposure is essential to prevent overexposed (too bright) or underexposed (too dark) images.
F – Focal Length:
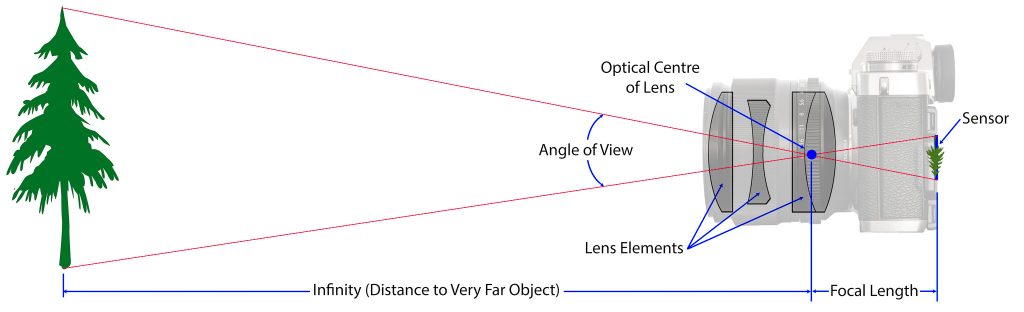
Focal length determines the field of view and magnification of a lens. Short focal lengths (e.g., 24mm) capture wide-angle shots, while longer focal lengths (e.g., 200mm) are used for telephoto shots.
G – Golden Hour:
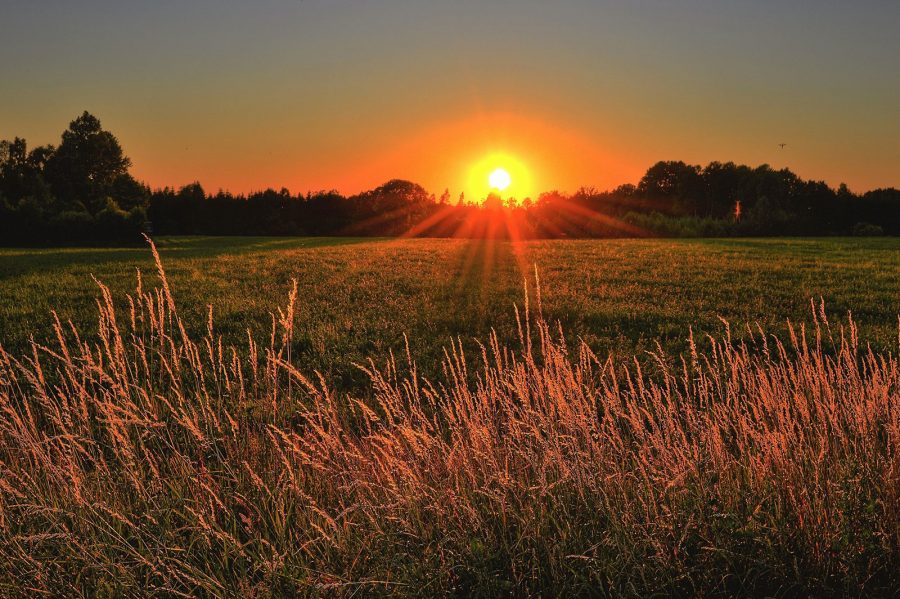

The Golden Hour is the period just after sunrise and just before sunset when the light is soft, warm, and perfect for photography. The long shadows and beautiful tones during this time add a magical touch to images.
H – Histogram:
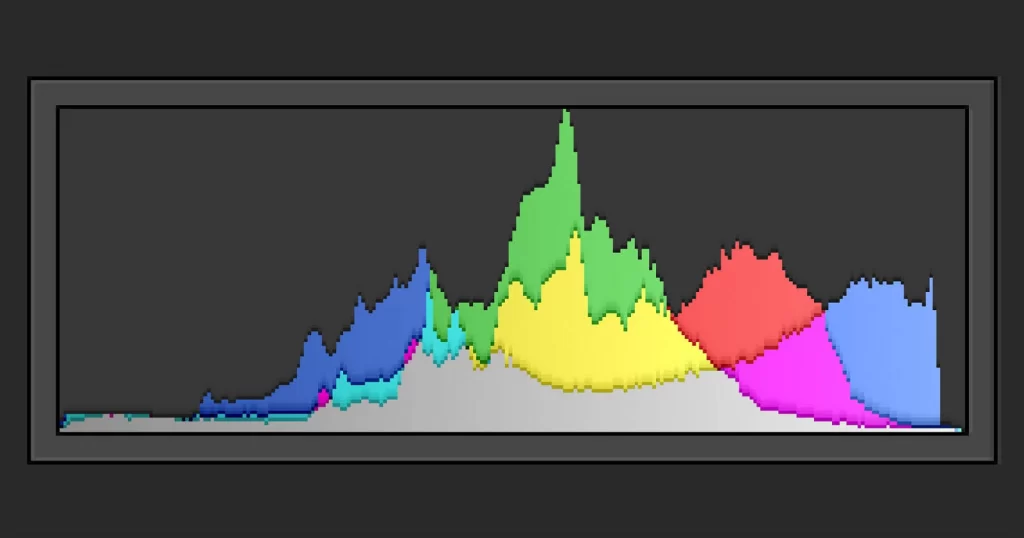
The histogram is a graphical representation of the tonal distribution in an image. It helps photographers analyze exposure and avoid losing details in shadows or highlights.
I – ISO:

ISO determines the camera sensor’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO settings are useful in low-light situations, but they can introduce noise/grain in the image.
J – JPEG:

JPEG is a common image file format used in photography. It employs compression to reduce file size but may sacrifice some image quality.
K – Kelvin:
The Kelvin scale is used to measure color temperature in photography. It allows you to adjust white balance and achieve accurate colors in different lighting conditions.
L – Long Exposure:
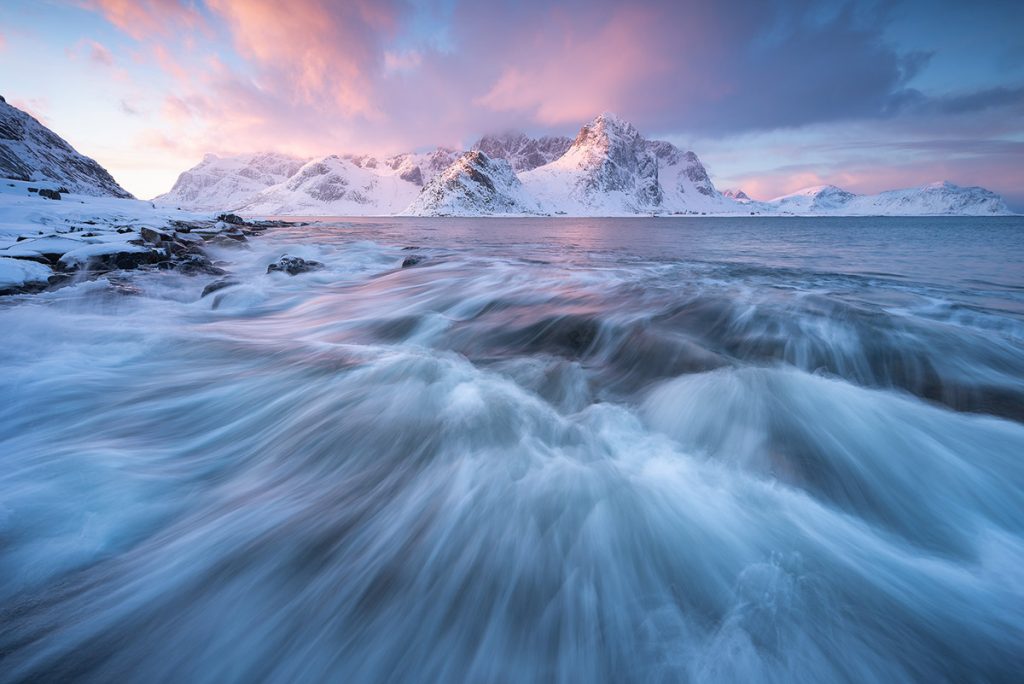

Long exposure involves using slower shutter speeds to capture motion or create surreal effects like light trails or smooth water in landscapes.
M – Macro:
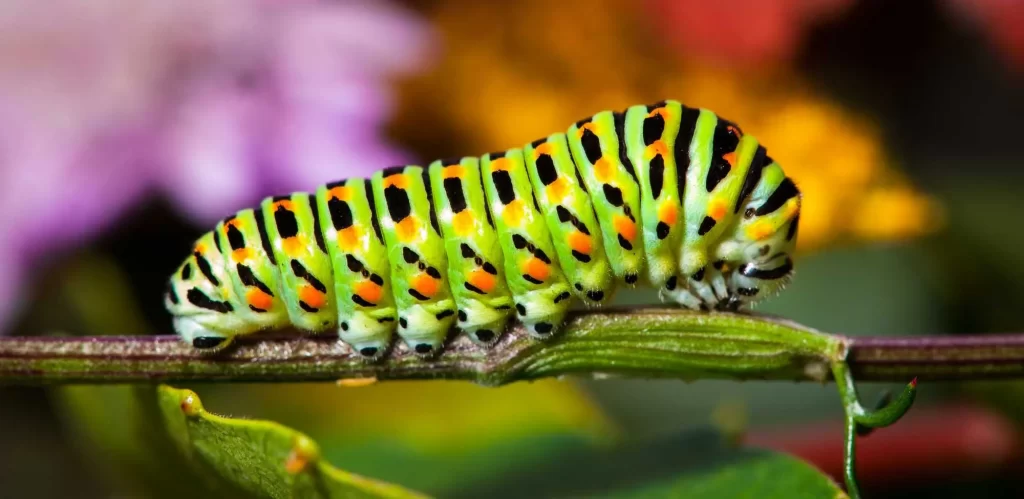

Macro photography focuses on capturing small subjects or details with extreme close-up shots. It reveals intricate patterns and textures not easily seen with the naked eye.
N – ND Filter:
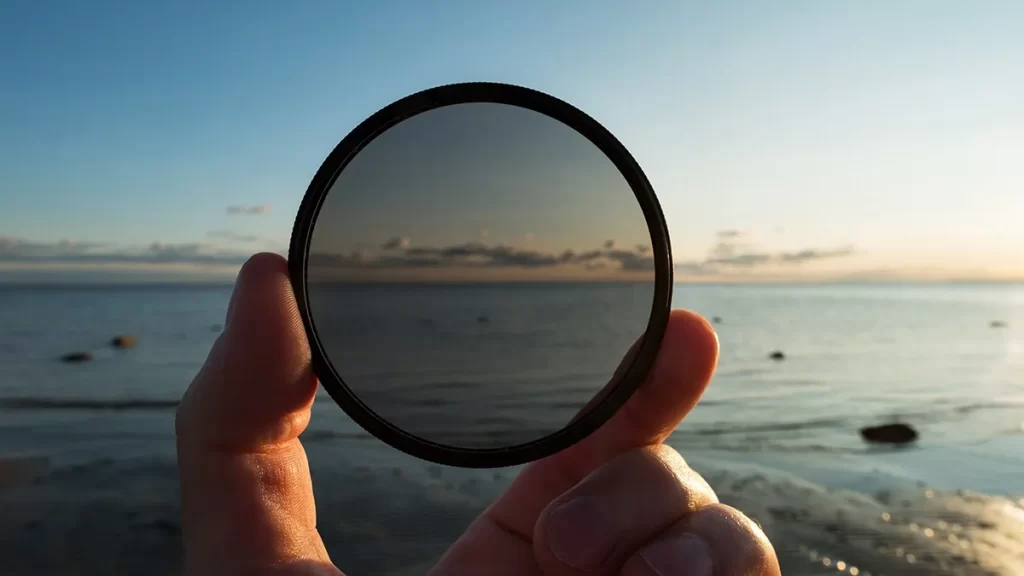

A Neutral Density filter reduces the amount of light entering the lens, allowing for longer exposures or wider apertures in bright conditions.
O – Overexposure:

Overexposure occurs when too much light enters the camera, resulting in loss of detail in the highlights.
P – Post-Processing:
Post-processing is the editing and enhancement of photographs using software like Adobe Lightroom or Photoshop. It allows photographers to fine-tune colors, contrast, and sharpness.
Q – Quality of Light:
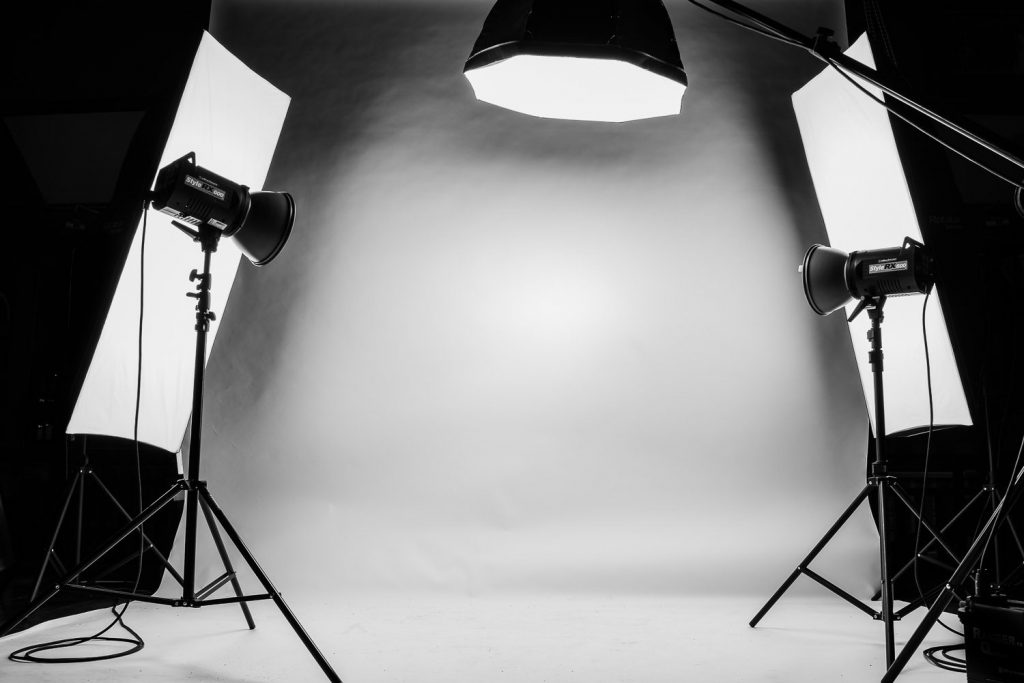

Understanding the quality of light is crucial in photography. Soft light from overcast skies can produce flattering portraits, while harsh light on a sunny day might create strong shadows.
R – Rule of Thirds:
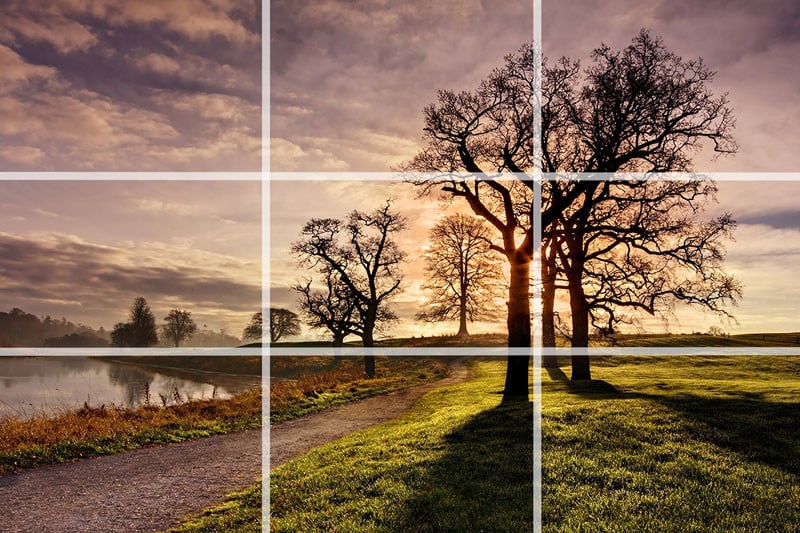

The Rule of Thirds is a compositional guideline where the image is divided into nine equal parts using two horizontal and two vertical lines. Placing key elements along these lines or their intersections often creates visually pleasing results.
S – Shutter Speed:

Shutter speed controls the amount of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Fast shutter speeds freeze motion, while slow shutter speeds create motion blur.
T – Tripod:
A tripod is a three-legged support that stabilizes the camera, preventing camera shake and allowing for longer exposures.
U – Underexposure:

Underexposure occurs when not enough light reaches the camera sensor, resulting in dark images with lost details in shadows.
V – Viewfinder:
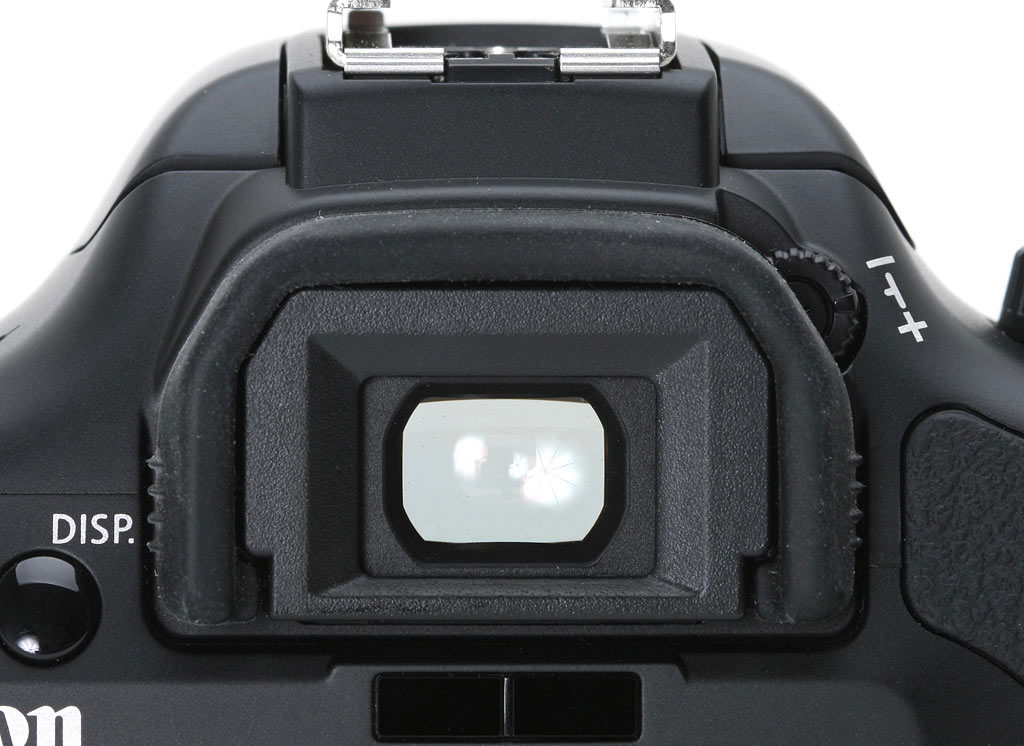

The viewfinder is a small window through which the photographer composes the shot by framing the scene.
W – White Balance:
White balance adjusts the color temperature to ensure accurate representation of colors in different lighting conditions.
X – X-sync:
X-sync refers to the synchronization of the flash with the camera’s shutter, ensuring that the flash fires at the right moment.
Y – Yearning for Perfection:
Photography is an art, and like all art forms, it involves continuous learning and a desire for perfection. Embrace the journey and strive to improve your skills with every shot.
Z – Zoom Lens:
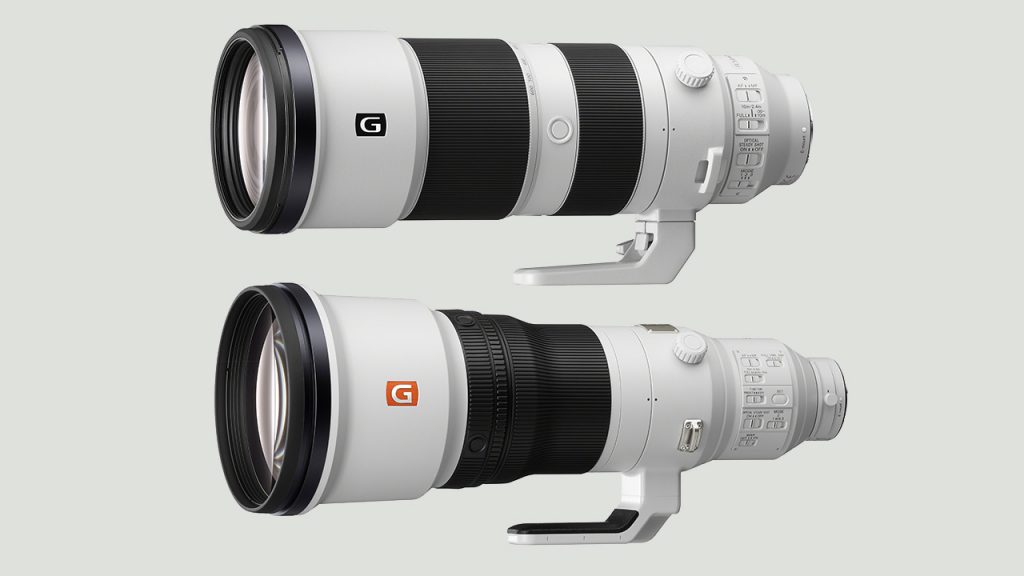

A zoom lens allows for variable focal lengths, providing flexibility to capture subjects at different distances without changing lenses.
In conclusion, photography is a versatile and expressive medium that enables us to capture moments, emotions, and the beauty of the world around us. Understanding the A-Z of photography empowers you to unlock your creativity and tell unique visual stories. Whether you’re capturing breathtaking landscapes, candid portraits, or intriguing macro shots, photography allows you to share your perspective with the world through the lens of your camera. So, grab your camera, experiment with different techniques, and let your imagination run wild as you embark on an exciting photographic journey!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
